South African Competition Commission Concludes Investigation into the AB In-Bev/SABMiller deal and Recommends that the Merger be Approved Subject to Conditions
On 31 May 2016, the South African Competition Commission (SACC) recommended that that the Anheuser-Busch Inbev/ SABMiller merger be approved subject to various conditions relating to both competition and public interest concerns.
 From a procedural aspect, the SACC’s recommendations are made to the South African Competition Tribunal, the adjudicative body ultimately responsible for approving a merger.
From a procedural aspect, the SACC’s recommendations are made to the South African Competition Tribunal, the adjudicative body ultimately responsible for approving a merger.
The SACC’s recommendations are not binding on the merging parties or the Tribunal. To the extent that the merging parties, or third parties, are concerned about the merger or the SACC’s recommendations, they may elect to participate in the hearing before the Tribunal.
In cases where neither the merging parties nor any third parties contest the SACC’s recommendations, the Tribunal usually rubber stamps the SACC’s recommendations.
We note that in terms of the SACC’s proposed recommendations, that the merging parties have made numerous undertakings to address the SACC’s concerns.
The following concerns and recommendations were proposed by the SACC:
- A divestiture of SABMiller’s shareholding in the Distell Limited Group (a competitor of SAB in the cider market) within three years of the closing date of the transaction;
- That no employees of the merged entity will be involved on the bottling operations of both Coca-Cola and PepsiCo and that no commercially sensitive information would be exchanged between employees in relation to these two soft drink entities;
- AB Inbev will continue supplying third parties with ‘tin metal crowns’ in South Africa as AB Inbev will own the only ‘tin metal supplier’ in South Africa post merger for a period of 5 years;
- AB Inbev should make at least 10% of its fridge space available, in small retail outlets or taverns, to competitors’ products to protect small beer producers;
- The development of a R1 billion fund which will be used, inter alia, to develop barley, hops and maize output in South Africa;
- No merger related retrenchments are to take place in South Africa, in perpetuity;
- AB Inbev will continue to supply certain products to small beer producers;
- AB Inbev will continue to ensure that it follows the same ratio of local production and will, itself, remain committed to sourcing products locally;
- Undertakings to ensure that the merging parties will, within two years after closing the merger, propose to the Commission and Government its plan on how to maintain black participation in the company and preserve equity;
- AB Inbev will continue to comply with the existing terms and conditions of the current agreements which exist between SABMiller and ‘owner-drivers’.
The merging parties have agreed to the majority of the conditions imposed on the merger. We note, however, that the SACC’s media statement does not make it clear that the merging parties have agreed to the divestiture recommendation. The merging parties have also not agreed to the proposed condition relating to a commitment to continue to supply small beer producers with hops and malt.
Accordingly, even in the absence of any third party intervention, this merger may still be contested before the Tribunal.
While the SACC’s official recommendations have not yet been published, it appears to us that a number of the concerns raised by the SACC relate to pre-existing concerns which are not merger specific. Furthermore, important aspect of the proposed recommendations, even those which have been agreed to between the parties, will be in perpetuity.
Furthermore, although what may appear to be a relatively innocuous proposed conditions which the merging parties shave agreed to, is that AB Inbev will respect the current existing contractual arrangements as between SABMiller and ‘owner drivers’. Approving a merger subject to such a condition poses an interesting conundrum. What happens in the event that there is contractual dispute between Ab-Inbev and owner drivers in the future? Will the Tribunal have jurisdiction to hear such disputes and could the merged entity be subject to penalties for breaching a condition of the merger, despite a contractual dispute which may have little if anything to do with the merger itself?
We have previously, here on Africanantitrust raised our concerns regarding the merger specificity of the R1 billion development fund. To access our previous article on this topic, please click here.
In our view, the Competition Tribunal should satisfy itself that the proposed conditions, even if agreed to between the merging parties, should address merger specific concerns and nothing more. A decision by the Tribunal is precedent setting and has an impact on the transparency and certainty of the merger control process in South Africa. When mergers are approved subject to conditions which go beyond merger specificity, uncertainty is created.


 the Confederation of African Football (CAF) to the Egyptian Economic Court for competition-law violations relating to certain exclusive marketing & broadcasting rights. In addition, it has been reported that the
the Confederation of African Football (CAF) to the Egyptian Economic Court for competition-law violations relating to certain exclusive marketing & broadcasting rights. In addition, it has been reported that the  Nigeria
Nigeria from U.S. and EU models, which usually do not afford amnesty to the lead perpetrators of hard-core antitrust violations, the CCM will also grant temporary immunity (during the half-year period from March 1 until the end of August 2017) not only to repentant participants but also to lead initiators of cartels, under the country’s Leniency Programme.
from U.S. and EU models, which usually do not afford amnesty to the lead perpetrators of hard-core antitrust violations, the CCM will also grant temporary immunity (during the half-year period from March 1 until the end of August 2017) not only to repentant participants but also to lead initiators of cartels, under the country’s Leniency Programme. Finally, COMESA will grow from 19 to 20 member states, welcoming Tunisia at the upcoming October 2017 summit: the
Finally, COMESA will grow from 19 to 20 member states, welcoming Tunisia at the upcoming October 2017 summit: the  The Competition Authority of Kenya (CAK) has recently announced that a number of proposed amendments to the Competition Act are currently pending before the National Assembly for consideration and approval.
The Competition Authority of Kenya (CAK) has recently announced that a number of proposed amendments to the Competition Act are currently pending before the National Assembly for consideration and approval. About half of these fees (approximately $1.5 million) were allocated to the national competition authorities in various COMESA states. However, competition authorities in COMESA member states – including Kenya, Zambia and Zimbabwe – continue to insist that merging parties lodge separate merger filings in their jurisdiction. This can add significant transactional costs – the filing fee in Kenya alone for a merger in which the merging parties combined generate more than KES 50 billion (about US $ 493 million) in Kenya is KES 2 million (nearly US $ 20 000). Since Kenya is one of the Continent’s largest economies, significant numbers of global transactions as well as those involving South African firms investing in African businesses are caught in the net.
About half of these fees (approximately $1.5 million) were allocated to the national competition authorities in various COMESA states. However, competition authorities in COMESA member states – including Kenya, Zambia and Zimbabwe – continue to insist that merging parties lodge separate merger filings in their jurisdiction. This can add significant transactional costs – the filing fee in Kenya alone for a merger in which the merging parties combined generate more than KES 50 billion (about US $ 493 million) in Kenya is KES 2 million (nearly US $ 20 000). Since Kenya is one of the Continent’s largest economies, significant numbers of global transactions as well as those involving South African firms investing in African businesses are caught in the net.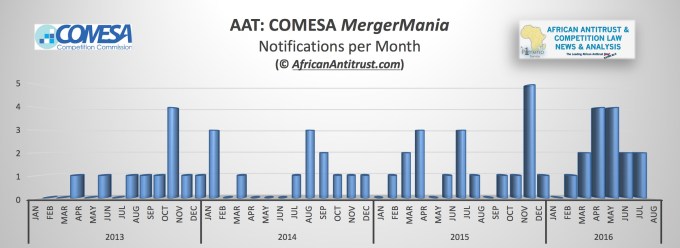
 From a procedural aspect, the SACC’s recommendations are made to the South African Competition Tribunal, the adjudicative body ultimately responsible for approving a merger.
From a procedural aspect, the SACC’s recommendations are made to the South African Competition Tribunal, the adjudicative body ultimately responsible for approving a merger.
 As we reported earlier this week, the previously granted extension of the competition authorities’ review was “widely suspected that the request for the extension is due to
As we reported earlier this week, the previously granted extension of the competition authorities’ review was “widely suspected that the request for the extension is due to 

 The R10-million administrative penalty is a record amount for gun-jumping, or the failure to notify the competition authorities of a merger. Previously, the highest penalty for a failure to notify was just over R1-million. The new record penalty follows numerous warnings by the Competition Commission (“Commission”) that it intended to materially increase penalties for failure to notify mergers — says Andreas Stargard, an antitrust practitioner with
The R10-million administrative penalty is a record amount for gun-jumping, or the failure to notify the competition authorities of a merger. Previously, the highest penalty for a failure to notify was just over R1-million. The new record penalty follows numerous warnings by the Competition Commission (“Commission”) that it intended to materially increase penalties for failure to notify mergers — says Andreas Stargard, an antitrust practitioner with